Useful information
- What is forwarding order and what type of information should it include?
- What is PGFR?
- What are INCOTERMS?
- Container types and parameters.
- Dangerous goods/cargo classification (ADR).
What is forwarding order and what type of information should it include?
In general, forwarding order means a document which is given to the forwarder by the principal and which obligates the forwarder to make or to arrange all forwarding services and the forwarder, as the mandatory, obligates to do or to arrange all those services for agreed price.
Basic information which should be included in forwarding order:
– principal`s precise name and contact details
– mandatory`s precise name and contact details
– shipper`s precise name and address
– consignee`s precise name and address
– cargo deatils such as: name, type, quantity, type of packaging, nett weight and gross weight, dimensions (in total and of each coil, part, piece if cargo consist of different parts, pieces)
– information regarding all documents, permissions and instructions obligated by law if cargo is dangerous type (ADR, IMO)
– level of temperature of cargo during transport
– loading/collection date (precise or as date interval)
– unloading/delivery date (precise or as date interval)
– is part delivery allowed
– necessary customs clearances
– cargo insurance
– terms of delivery (i.e. Incoterms, Combiterms etc.)
– type and time of sending notices
– precise instructions of filling transport documents
– instruction of sending documents
– agreed price for forwarding service.
What is PGFR?
PGFR is a shortcut for POLISH GENERAL FORWARDING RULES.
Those rules are prepared nad published by Polish International Freight Forwarders Association (PIFFA). Latest available version of PGFR is from 2010. It can be found on PIFFA website:
What are INCOTERMS?
INCOTERMS are a set of three-letter commercial terms published by the Interational Chamber Of Commerce . They are used in international trade transactions almost all over the world. They are related to common contractual sales practices. The INCOTERMS are intended primarily to clearly communicate the tasks, costs and risks associated with the transportation and delivery of goods.
Most recent version of INCOTERMS has been announced in 2010. It consists of 11 below described rules:
RULES FOR ANY MODE OR MODES OF TRANSPORT
EXW
EX WORKS (…named place of delivery)
According to this rule the seller deliver when he places goods at the disposal of the buyer at the seller`s premises or at another named place (i.e. works, factory, etc.). The seller is no obligated to load goods on any collecting vehicle and he does not need to custom clear goods for export, where such clearance is obligatory. EXW represents minimum obligation of the seler.
FCA
FREE CARRIER (…namef place of delivery)
According to this rule the seller delivers goods to the carrier or another person nominated by the buyer at the seller`s premises or another named place. FCA requires the seller to custom clear the goods for export, where such clearance is obligatory.
CPT
CARRIAGE PAID TO (…named place of destination)
According to this rule the seller delivers goods to the carrier or to another person nominated by the seller at an agreed place and that the seller is obligated to contract for and pay the cost of carriage necessary to bring the goods to the named place of destination.
CPT requires the seller to custom clear the goods for export, where such clearance is obligatory.
CIP
CARRIAGE AND INSURANCE PAID TO (…named place of destination) According to this rule the seller delivers the goods to the carrier or another person nominated by the seller at an agreed place and that the seller is obligated to contract for and pay the costs of carriage necessary to bring the goods to the named place of destination.The seller also arranges insurance cover against the buyer`s risk of loss of or damage to the goods during the carriage. CIP requires the seller to custom clear goods for export, where such clearance is obligatory.
DAT
DELIVERED AT TERMINAL (…named terminal at port or place of destination)
According to this rule the seller delivers when the goods, after they are unloaded from the arriving means of transport, are placed at the disposal of the buyer at a named terminal at the named port or place of destination. „Terminal” means any place, whether covered or not, such as quay, warehouse, container yard or road, rai lor air cargo terminal. DAT requires the seller to custom clear the good for export, where such clearance is obligatory.
DAP
DELIVERED AT PLACE (…named place of destination)
According to this rule seller delivers when the goods are place dat the disposal of the buyer on the arriving means of transport ready for unloading at the named place of destination.
DAP requires the seller to custom clear the goods for export, where such clearance is obligatory.
DDP
DELIVERED DUTY PAID (…named place of destination)
According to this rule the seller delivers the goods when they are placed at the disposal of the buyer, cleared for import at the arriving means of transport ready for unloading at the named place of destiantion.
DDP requires the seller to custom clear the goods for export, where such clearance is obligatory.
RULES FOR SEA AND INLAND WATERWAY TRANSPORT
FAS
FREE ALONGSIDE SHIP (… named port of shipment)
According to this rule the seller delivers when the goods are placed alongside the vessel (i.e. on a quay) nominated by the buyer at the named port of shipment.
FAS requires the seller to custom clear the goods for export, where such clearance is obligatory.
FOB
FREE ON BOARD (…named port of shipment)
According to this rule the seller delivers the goods on board the vessel nominated by the buyer at the named port of shipment or causes the goods to be delivered this way.
FOB requires the seller to custom clear the goods for export, where such clearance is obligatory.
CFR
COST AND FREIGHT (…named port of destination)
According to this rule the seller delivers the goods on board the vessel or causes the goods to be delivered this way. The seller is obligated to contract for and pay the costs and freight necessary to deliver the goods to the named port of destination. The seller is obligated to contract for and pay the costs and freight necessary to deliver the goods to the named port of destination.
CFR requires the seller to custom clear the goods for export, where such clearance is obligatory.
CIF
COSTS, INSURANCE AND FREIGHT (…named port of destination)
According to this rule the seller delivers the goods on board the vessel or causes the goods to be delivered this way. The seller also arranges insurance cover against the buyer`s risk of loss of or damage to the goods during the carriage.
CIF requires the seller to custom clear the goods for export, where such clearance is obligatory.
To learn more about INCOTERMS please visit ICC`s website: http://www.iccwbo.org/
Container types and parameters.
20` container:
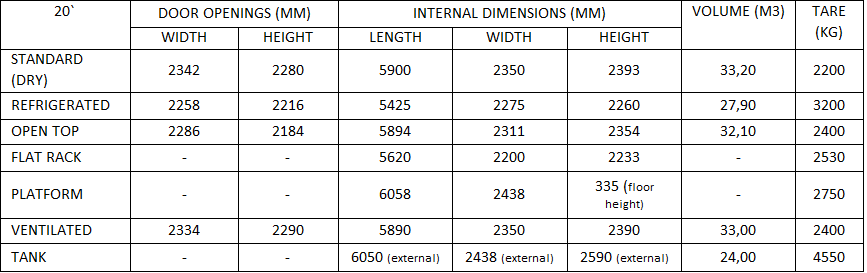
40` container:
Dangerous goods/cargo classification (ADR).
The European Agreement concerning the International Carriage of Dangerous Goods by Road (ADR)
Class Descrption
1. EXPLOSIVE MATERIALS AND OBJECTS
2. GASES
3. FLAMMABLE LIQUIDS
4.1 FLAMMABLE SOLIDS
4.2 SELF-COMBUSTIBLE MATERIALS
4.3 MATERIALS THAT EMIT A FLAMMABLE GAS IN CONTACT WITH WATER
5.1 OXIDISING AGENT
5.2 ORGANIC PEROXIDE
6.1 POISONOUS MATERIAL
6.2 BIOHAZARD
7 RADIOACTIVE MATERIAL
8 CORROSIVE MATERIAL
9 MISCELLANEOUS DANGEROUS MATERIALS AND OBJECTS






